Advancing Severe Weather Detection: The Rise of Dual Polarization Radar in the US

Weather radar has always been a cornerstone of meteorological observation and forecasting. Yet, traditional radar systems, while effective, were limited in their ability to decipher the complexities within storms, often leaving meteorologists with an incomplete picture. The advent of dual polarization radar technology marked a paradigm shift, ushering in an era of enhanced precision and understanding in severe weather detection and warnings.
Understanding the Dual Pol Advantage:
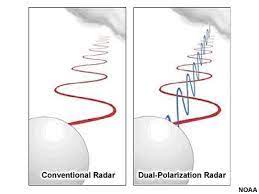
Traditional weather radars transmit and receive horizontally polarized waves, meaning the waves vibrate parallel to the ground. This provides information about the location and intensity of precipitation but lacks the ability to discern the size, shape, and variety of particles within a storm. Dual polarization technology builds upon this foundation by introducing a second dimension – vertical polarization. By transmitting and receiving both horizontally and vertically polarized waves, dual pol radar paints a more comprehensive picture of the storm environment.
Transforming Tornado Detection:
One of the most significant benefits of dual pol technology lies in its ability to enhance tornado detection and warnings. Traditional radar could identify areas of rotation within a storm, suggestive of a possible tornado. However, confirming the presence of a tornado often relied on visual sightings or the detection of debris lofted into the air, both of which could be unreliable or delayed.
Dual pol radar brought a game-changing advantage: the ability to detect debris fields associated with tornadoes. When a tornado is on the ground, it lifts a variety of objects – from tree limbs and building materials to vehicles and even larger structures. These objects scatter radar waves differently than raindrops or hailstones, creating a distinct signature that dual pol radar can identify. This capability allows meteorologists to confirm the presence of a tornado with greater confidence and issue more timely and accurate warnings, potentially saving lives.
Sharper Images, Clearer Insights:
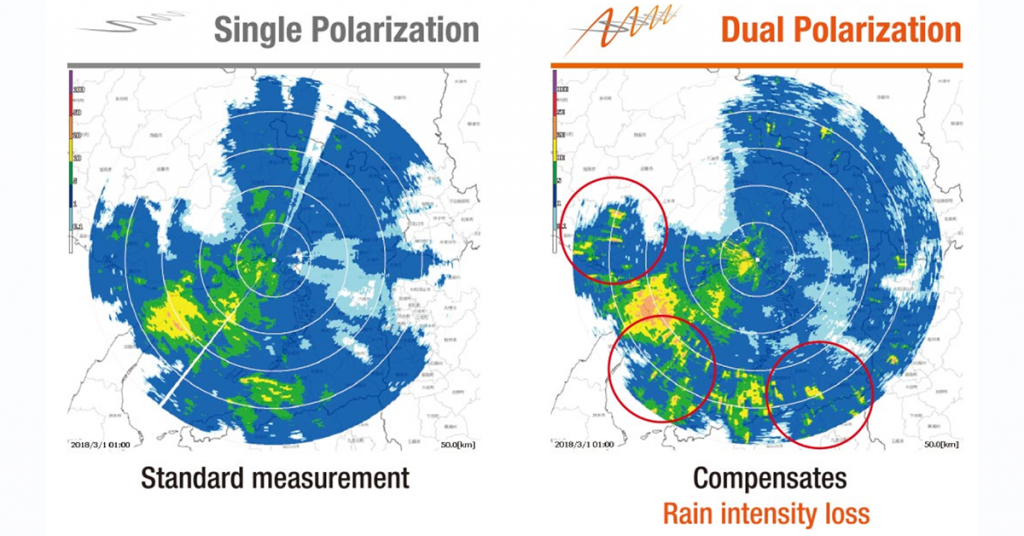
Beyond debris detection, dual pol technology enhances the overall resolution and clarity of radar data. By analyzing the way horizontally and vertically polarized waves interact with precipitation particles, meteorologists can estimate the size and shape of raindrops, hailstones, and snowflakes. This information provides valuable insights into the intensity of precipitation, the potential for flooding, and the type of winter weather expected.
A Nationwide Upgrade: The Dual Pol Rollout:
Recognizing the transformative potential of dual polarization technology, the National Weather Service (NWS) embarked on an ambitious endeavor to upgrade its entire network of radars across the United States. The rollout, initiated in 2010 and completed in 2013, involved retrofitting existing radars with dual pol capabilities, ensuring comprehensive coverage for the nation.
This nationwide upgrade has yielded substantial improvements in severe weather detection and warnings. Studies have shown a significant increase in lead times for tornado warnings and a reduction in false alarms, underscoring the life-saving potential of this technology.
Beyond Tornadoes: A Multifaceted Tool:
While the impact of dual pol radar on tornado warnings has been profound, its benefits extend far beyond this realm. The technology has proven invaluable for:
- Improved Rainfall Estimates: By providing more accurate measurements of rainfall amounts, dual pol data enhances flash flood warnings and supports better water resource management.
- Winter Weather Monitoring: The ability to differentiate between various types of frozen precipitation, such as snow, sleet, and freezing rain, leads to more precise winter storm forecasts and improved road condition monitoring.
- Aviation Safety: Dual pol radar aids in identifying hazardous weather phenomena for aviation, including icing conditions and turbulence, contributing to safer air travel.
